Which Cloud Model is Best?
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the different cloud models is crucial for business scalability, cost management, and security.
- Public, Private, and Hybrid clouds each have their unique advantages and disadvantages.
- Choosing the right cloud model depends on specific business needs, budget, and technical requirements.
- Startups may prefer public clouds for cost-effectiveness, while larger enterprises might opt for hybrid solutions.
- A comprehensive decision guide can aid businesses in selecting the most suitable cloud model.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Cloud Computing Models
- Choosing a Cloud Computing Model
- Best Cloud Model for Business
- Public vs Private Cloud for Startups
- Cloud Model Decision Guide
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
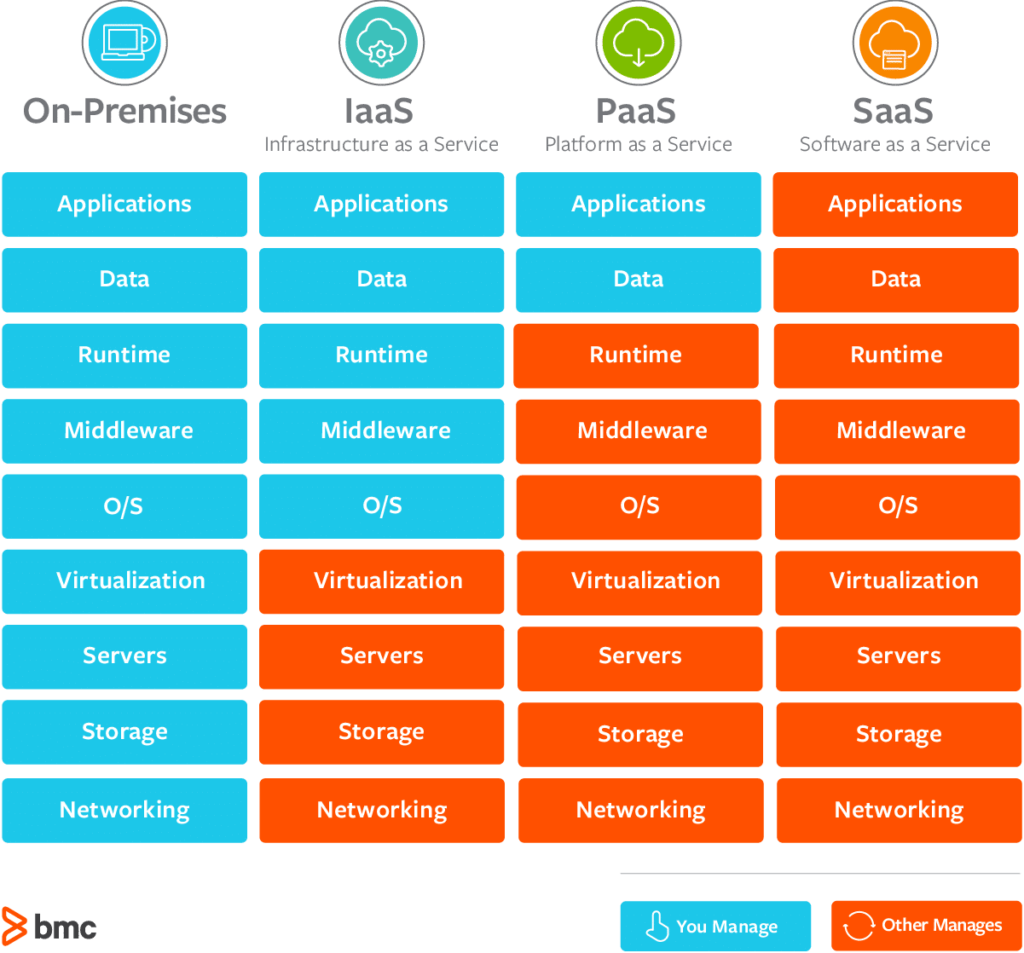
*Which cloud model is best?* This is a fundamental question for businesses venturing into cloud computing. Selecting the right cloud model is pivotal for business success, influencing scalability, cost efficiency, and security. There are primarily three cloud models available: public, private, and hybrid. This guide aims to assist you in making an informed decision on how to choose the right cloud model based on your specific needs.
Understanding Cloud Computing Models
Public Cloud
Public clouds are operated by third-party providers delivering computing resources over the internet. They offer a shared infrastructure used by multiple organizations and typically follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model. Public clouds are managed and maintained by the cloud provider, allowing businesses to focus on their core activities without worrying about infrastructure maintenance.
- Advantages:
- Low upfront costs.
- High scalability to accommodate business growth.
- No maintenance required from the business side.
- Disadvantages:
- Less control over the infrastructure.
- Potential security concerns due to shared resources.
Incorporate research findings on public clouds: Research on Public Clouds
Private Cloud
Private clouds are dedicated environments used by a single organization. They offer a dedicated infrastructure that can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds are managed by internal IT teams or a managed service provider, providing greater control and customization options.
- Advantages:
- Greater control and customization options.
- Enhanced security and privacy.
- Meets strict compliance requirements for certain industries.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher costs compared to public clouds.
- Requires IT expertise to manage and maintain.
Incorporate research findings on private clouds: Research on Private Clouds
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments, allowing integration between the two. This model enables workloads to move seamlessly based on business needs, providing flexibility to use the most suitable platform for each specific workload.
- Advantages:
- Balances control and scalability.
- Optimizes existing infrastructure investments.
- Supports gradual cloud migration without full commitment.
- Disadvantages:
- More complex to manage due to integration requirements.
- Requires robust networking and management solutions.
Incorporate research findings on hybrid clouds: Research on Hybrid Clouds
Choosing a Cloud Computing Model
Assessing Business Needs
Define specific business requirements around performance, security, and compliance. Identify which applications and workloads are suitable for the cloud and consider future growth plans to determine how different cloud models can support them.
Evaluating Cost Considerations
Conduct a cost-benefit analysis of different cloud models over time, factoring in both direct costs (e.g., subscription fees) and indirect costs (e.g., maintenance). Align budget constraints with financial planning to determine affordability.
Security and Compliance
Assess security requirements and the organization’s risk tolerance. Review industry-specific compliance needs and regulations, and evaluate the security features and compliance capabilities of each cloud model.
Scalability and Flexibility
Determine the scalability needs for computing resources based on business growth. Assess how flexible the cloud environment needs to be to adapt to changing business demands, and evaluate the ability of each cloud model to scale resources up or down efficiently.
Technical Requirements
Review compatibility with existing systems, applications, and IT infrastructure. Assess the in-house technical capabilities required to manage and maintain the cloud environment, and consider support and maintenance needs, including vendor support options.
Best Cloud Model for Business
Define criteria for determining the best cloud model for business based on:
- Business Size and Type: Different models suit startups, SMEs, and large enterprises differently.
- Industry and Compliance Requirements: Certain industries may have stricter compliance needs influencing the choice.
- Existing IT Infrastructure: Integration with current systems can affect the suitability of a cloud model.
- Budget and Resources: Financial constraints and available resources play a critical role.
- Security Needs: Higher security requirements may necessitate private or hybrid models.
- Scalability Requirements: Businesses anticipating rapid growth may benefit from highly scalable public or hybrid models.
Provide case studies or examples of successful cloud model implementations in various business contexts:
- Example 1: A large enterprise utilizing a hybrid cloud for compliance and scalability.
- Example 2: A small business leveraging a public cloud for cost-effective growth.
Public vs Private Cloud for Startups
Public Cloud for Startups
Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs making it financially accessible for startups.
- Easy scalability to support growth without significant infrastructure investment.
- Minimal maintenance required, allowing startups to focus on core business activities.
Challenges:
- Less control over the underlying infrastructure.
- Potential security concerns due to shared resources with other organizations.
Incorporate research findings: Public Cloud Research for Startups
Private Cloud for Startups
Advantages:
- Enhanced security and control over the cloud environment.
- Customization options to tailor the infrastructure to specific startup needs.
Drawbacks:
- Higher costs associated with setting up and maintaining a private cloud.
- More complex to manage, requiring technical expertise which may be limited in startups.
Incorporate research findings: Private Cloud Research for Startups
Guidance on Selection:
Provide criteria for startups to consider when choosing between public and private clouds, such as funding, growth projections, and security needs. Suggest scenarios where one model may be more advantageous than the other.
Cloud Model Decision Guide
Provide a step-by-step guide to making an informed cloud model decision:
- Assess Your Business Needs and Goals
- Define what you aim to achieve with cloud adoption.
- Evaluate Your Budget and Resources
- Analyze financial constraints and available resources.
- Review Security and Compliance Requirements
- Ensure the chosen model meets necessary security standards and regulatory compliance.
- Determine Scalability Needs
- Assess how much and how quickly you need to scale your resources.
- Consider Existing Infrastructure and Applications
- Check compatibility and integration with current systems.
- Assess In-House IT Capabilities
- Evaluate your technical team’s ability to manage the cloud environment.
- Review Vendor Options and Offerings
- Compare different cloud service providers and their offerings.
- Analyze Total Cost of Ownership for Each Model
- Calculate long-term costs associated with each cloud model.
- Start with a Pilot Project if Possible
- Test the chosen cloud model on a small scale before full implementation.
- Re-evaluate as Your Needs Evolve
- Continuously assess and adjust your cloud strategy as your business grows and changes.
Checklist of Factors to Consider:
- Business objectives alignment
- Financial implications
- Security and compliance needs
- Scalability and flexibility requirements
- Technical compatibility and support
- Vendor reliability and support services
Tools and Resources:
- Recommend tools for cloud cost analysis, security assessment, and performance monitoring.
- Provide links to resources or templates that can aid in the decision-making process.
Incorporate research findings: Cloud Decision Guide Research
Conclusion
In summary, selecting which cloud model is best is a critical decision that impacts various aspects of your business. By carefully evaluating your specific needs using the provided cloud model decision guide, you can determine the best cloud model for business that aligns with your goals. Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all answer; the optimal cloud model depends on individual business requirements. Utilize this guide to make informed choices that ensure long-term success and scalability for your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is cloud computing secure? Cloud providers implement strict security measures, but users must also follow best practices.
- What are the top cloud providers? The leading providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Can small businesses benefit from cloud computing? Yes! Cloud services offer affordable, scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes.