What Are Cloud Models? Comprehensive Guide to Cloud Computing Models Explained
Estimated reading time: 15 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing offers on-demand access to IT resources over the Internet, enhancing scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Understanding different cloud models is crucial for making informed decisions about cloud service and deployment strategies.
- The primary cloud service models include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- The main cloud deployment models are Public, Private, Hybrid, and Community Clouds, each catering to specific organizational needs.
- Selecting the appropriate cloud architecture model is vital for optimizing performance, security, and cost-efficiency.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Introduction to Cloud Models
- Cloud Computing Models Explained
- Types of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Service Models
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Cloud Architecture Models
- Use Cases for Different Cloud Models
- Benefits and Challenges of Each Cloud Model
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
What are cloud models? Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. It plays a significant role in modern technology by offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud models serve as frameworks that define how cloud services are delivered and deployed. This blog post focuses on answering the primary question: What are cloud models?
Introduction to Cloud Models
Understanding cloud models is essential for businesses and IT professionals to make informed decisions about their cloud strategies. Cloud models are broadly categorized into service models, deployment models, and architecture models. Grasping the various cloud computing models explained helps organizations select the right cloud strategy tailored to their specific needs.
Cloud Computing Models Explained
Cloud computing models explained encompass the various frameworks that structure how cloud services are delivered. The three primary cloud service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Additionally, there are four main cloud deployment models: Public, Private, Hybrid, and Community. These models facilitate different cloud services and deployments, allowing organizations to choose based on their specific requirements.
Types of Cloud Computing
The main types of cloud computing include:
- Service Delivery Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- Deployment Models (Public, Private, Hybrid, Community)
These types differ based on service delivery (what is provided) and infrastructure (how it is deployed). The table below visualizes the types of cloud computing for easier understanding:
| Type | Service Delivery | Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|
| IaaS | Provides virtualized computing resources | Public or Private Cloud |
| PaaS | Provides a platform for developers to build applications | Public, Private, or Hybrid Cloud |
| SaaS | Provides fully functional software applications | Public Cloud |
| Deployment | Defines where and how the cloud infrastructure is deployed | Public, Private, Hybrid, Community Clouds |
Cloud Service Models
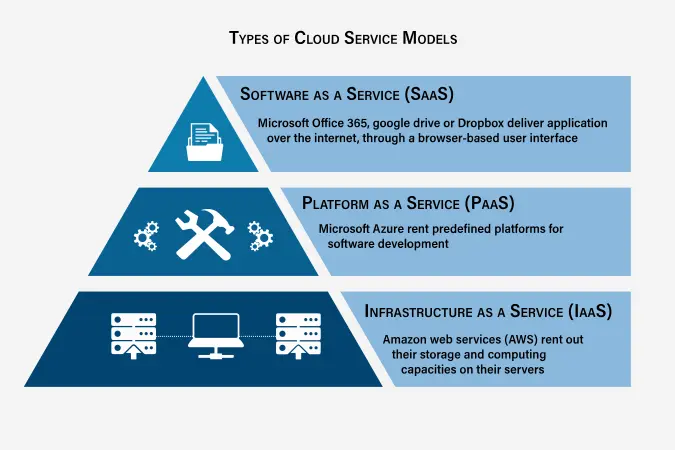
Cloud service models define the level of control and management between the provider and the user. The primary cloud service models include:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides on-demand access to fundamental computing resources like servers, storage, and networking. Key features include scalable resources, pay-as-you-go pricing, and self-service provisioning. Common use cases for IaaS are website hosting, backup and recovery, and high-performance computing. [15]
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) delivers a platform for customers to develop, run, and manage applications without maintaining the underlying infrastructure. Key features include built-in development tools, automated deployment, and scalable infrastructure. Common use cases include application development, API development and management, and business analytics. [14]
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) provides access to software applications over the internet, managed by the provider and accessed via web browsers. Key features include automatic updates, accessibility from any device, and a subscription-based model. Common use cases include customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and collaboration tools. [14]
Comparison of Service Models
Comparing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in terms of control, flexibility, and use cases:
| Service Model | Control | Flexibility | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| IaaS | High control over infrastructure | Highly flexible | Website hosting, storage, networking |
| PaaS | Control over application deployment | Moderately flexible | App development, testing, deployment |
| SaaS | Minimal control, provider manages most aspects | Least flexible | Email, CRM, collaboration tools |
Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud deployment models define the environment in which cloud services operate. The primary deployment models include:
Public Cloud
Public Cloud refers to cloud services offered over the internet by third-party providers. Characteristics and benefits include cost-effectiveness, high scalability, and minimal maintenance. Suitable scenarios for Public Clouds include startups, small businesses, web-based applications, and development and testing environments. [20]
Private Cloud
Private Cloud is a dedicated cloud environment exclusively used by a single organization. It offers enhanced security and privacy, greater control over infrastructure, and is customizable to specific needs. Suitable scenarios include organizations with strict regulatory requirements, large enterprises with sensitive data, and industries with specific compliance needs. [Wikipedia – Cloud Computing]
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. Characteristics and benefits include flexibility to run workloads in optimal environments, cost-effective use of public cloud for non-sensitive operations, and the ability to scale using public cloud resources. Suitable scenarios are organizations with fluctuating workloads, businesses managing both sensitive and non-sensitive data, and companies transitioning from private to public clouds. [Wikipedia – Cloud Computing]
Community Cloud
Community Cloud is a shared cloud environment among several organizations with common concerns or missions. Characteristics and benefits include shared infrastructure costs, a collaborative environment, and compliance with industry-specific requirements. Suitable scenarios include government agencies, healthcare organizations, and educational institutions. [Wikipedia – Cloud Computing]
Decision-Making Process
When choosing a cloud deployment model, consider factors such as security requirements, budget constraints, scalability needs, and compliance regulations. The following flowchart guides you through the selection process:

Cloud Architecture Models
Cloud architecture models refer to the structural design of cloud computing systems, encompassing various components and their interactions. The main components include:
- Front-end Platforms: Client-side interfaces such as web browsers or mobile apps.
- Back-end Platforms: Servers, storage, and networking managed by cloud providers.
- Cloud-Based Delivery Networks: Infrastructure that delivers cloud services to users.
Best practices in designing cloud architectures include:
- Ensuring scalability to handle varying loads.
- Implementing robust security measures to protect data.
- Optimizing for performance and cost-efficiency.
Use Cases for Different Cloud Models
Various industries implement different cloud models based on their unique needs:
- Healthcare: Use Hybrid Clouds for managing patient data and research. For example, hospitals may use Private Clouds for sensitive patient information while leveraging Public Clouds for non-critical applications.
- Finance: Utilize SaaS for customer relationship management (CRM) and analytics. Banks may use SaaS platforms for managing customer data and financial analysis.
- E-commerce: Implement IaaS for scalable web hosting during peak seasons. Online retailers may scale their infrastructure using IaaS providers like AWS or Azure during holiday sales.
- Education: Employ Community Clouds for shared resources among educational institutions. Universities may collaborate on research projects using a Community Cloud.
- Additional Use Cases: Government agencies using Private or Community Clouds for secure data management; Startups leveraging PaaS for rapid application development without heavy infrastructure investments.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Cloud Model
Benefits
- Cost Savings: Reduced infrastructure investments and operational costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Ability to scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Accessibility: Access resources from anywhere, fostering collaboration.
- Innovation Enablement: Faster deployment of applications and services.
Challenges
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Especially prevalent in Public Clouds; robust security measures are needed.
- Potential Vendor Lock-In: Dependence on a single cloud provider’s services and infrastructure.
- Compliance Issues: Navigating regulatory requirements in industries like healthcare and finance.
- Performance Variability: Dependence on internet connectivity and provider performance.
Analysis by Cloud Model
| Cloud Model | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Cost-effective, highly scalable | Security concerns, less control over data |
| Private Cloud | Enhanced security, greater control | Higher costs, requires in-house management |
| Hybrid Cloud | Flexibility, optimized resource usage | Complex management, potential integration issues |
| Community Cloud | Shared costs, collaborative environment | Limited to specific groups, potential for resource contention |
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored cloud models, including the different service, deployment, and architecture models. Selecting the right cloud model is crucial based on your organization’s specific needs, goals, and constraints. Understanding what are cloud models empowers businesses to leverage cloud computing effectively for innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage. Assess your requirements carefully to choose the most suitable cloud model for your operations.
Additional Resources
For further reading on cloud computing models explained and introduction to cloud models, explore the following resources:
- Understanding Cloud Computing: A Beginner’s Guide
- Advanced Cloud Architecture Design
- Comparing Cloud Service Providers
Additionally, consider delving into related topics such as:
- Cloud Security Best Practices
- Migrating to the Cloud: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Future Trends in Cloud Computing
Tools and resources for a deeper understanding include cloud model comparison charts and architecture design tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is cloud computing secure? Cloud providers implement strict security measures, but users must also follow best practices to ensure data protection.
- What are the top cloud providers? The leading providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Can small businesses benefit from cloud computing? Yes! Cloud services offer affordable, scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes.