Shared Responsibility in Cloud Computing: Ensuring Robust Cloud Security
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Shared responsibility in cloud computing is essential for maintaining robust security and compliance.
- Understanding the cloud security responsibility model helps delineate security duties between providers and customers.
- Implementing best practices ensures effective management of shared responsibility in cloud environments.
- Collaboration between cloud providers and customers is vital for comprehensive security.
- Addressing common challenges enhances the security posture of cloud deployments.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Shared Responsibility in Cloud
- Cloud Security Responsibility Model
- Cloud Provider and Customer Responsibilities
- Cloud Computing Security Roles
- Best Practices for Managing Shared Responsibility
- Common Challenges and Solutions
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Importance of Understanding Shared Responsibility for Cloud Security
The concept of shared responsibility in cloud computing is pivotal for maintaining robust security and compliance when utilizing cloud services. Understanding this model is crucial as cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it essential to comprehend the dynamics of security in such environments. Without a clear understanding of shared responsibilities, organizations may face vulnerabilities and compliance issues.
Overview of Cloud Computing and Its Widespread Adoption
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including storage, processing power, and networking—over the internet. This paradigm allows businesses and individuals to access and utilize resources without the need for physical infrastructure. The various types of cloud services include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). The adoption of cloud computing has been growing across industries due to its ability to provide scalable and flexible solutions tailored to specific business needs.
Understanding Shared Responsibility in Cloud
Definition of Shared Responsibility in Cloud Computing
Shared responsibility in cloud computing refers to the division of security obligations between cloud service providers (CSPs) and their customers. According to the Cloud Security Alliance, this model ensures that both parties are aware of their roles in protecting data and maintaining compliance.
Explanation of the Concept and Its Relevance to Cloud Services
In cloud environments, both CSPs and customers play critical roles in securing data and systems. This contrasts with traditional on-premises IT setups where organizations have full control over security measures. By adopting a shared responsibility model, cloud security becomes a collaborative effort. Darktrace highlights that understanding shared responsibilities is key to effective cloud security, ensuring that all potential vulnerabilities are addressed collaboratively.
Differences Between Traditional IT Security and Cloud Security
Traditional IT security models place the entire responsibility for security on the organization. In contrast, cloud security employs a shared responsibility model where security tasks are divided between CSPs and customers. This shift requires organizations to clearly delineate responsibilities to avoid security gaps. The cloud security responsibility model outlines these distinctions, emphasizing the need for clear responsibility allocation based on different cloud service types.
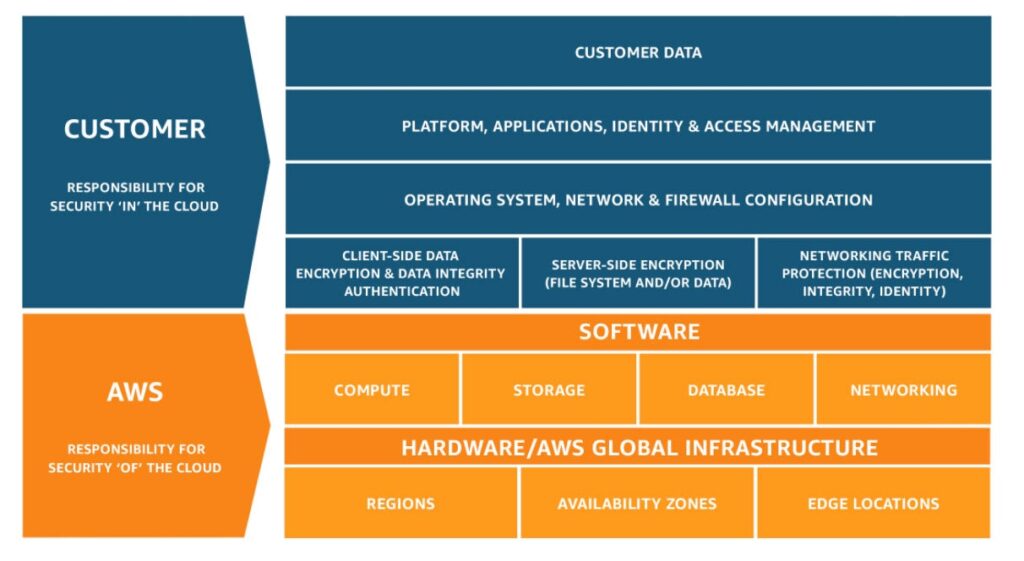
Cloud Security Responsibility Model
Description of the Cloud Security Responsibility Model
The cloud security responsibility model defines the specific security duties of both CSPs and their customers. This model ensures that each party knows their obligations, reducing the risk of security oversights and enhancing overall cloud security posture.
Components of the Model and Division of Responsibilities
The model breaks down responsibilities into various components, often aligned with different layers of the cloud stack. For example, in Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), CSPs manage the physical infrastructure, while customers handle operating systems, applications, and data security. Understanding these divisions is critical for maintaining secure cloud environments.
Comparison of Responsibility Models Based on Cloud Service Types (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): CSP manages physical infrastructure security. Customers secure operating systems, applications, and data. CoreStack
Platform as a Service (PaaS): CSP secures underlying infrastructure and platform. Customers manage application security and data. CoreStack
Software as a Service (SaaS): CSP handles most security aspects, including application security. Customers focus on data security and access management. CoreStack
Cloud Provider and Customer Responsibilities
Responsibilities of Cloud Providers
Cloud providers are responsible for:
- Physical security of data centers.
- Network infrastructure security.
- Hypervisor security.
- Service availability and reliability.
Responsibilities of Cloud Customers
Cloud customers are responsible for:
- Data protection and encryption.
- Identity and access management.
- Application security.
- Operating system patching (in IaaS models).
- Network and firewall configurations.
Examples of Tasks Each Party is Accountable For
Cloud Providers: Ensuring physical data center security, maintaining uptime.
Customers: Configuring security groups, managing user access.
Cloud Computing Security Roles
Explanation of Various Cloud Computing Security Roles within the Shared Responsibility Framework
Within the shared responsibility framework, several security roles are crucial for maintaining cloud security. These roles ensure that all aspects of security are addressed comprehensively.
Roles of Different Stakeholders
IT Administrators: Manage cloud resources and configure security settings.
Security Teams: Oversee overall security strategy and conduct risk assessments.
End-Users: Follow security best practices and organizational policies.
Collaboration to Maintain a Secure Cloud Environment
Effective collaboration among different roles is essential for maintaining a secure cloud environment. IT administrators, security teams, and end-users must communicate and coordinate their efforts, ensuring that security measures are consistently applied and updated across the cloud infrastructure.
Best Practices for Managing Shared Responsibility
Strategies for Customers to Effectively Manage Their Security Responsibilities
Understand Security Obligations:
Clearly define responsibilities for each cloud service used.
Implement Strong Identity and Access Management:
Use multi-factor authentication and least privilege principles.
Regularly Audit and Monitor Cloud Environments:
Conduct periodic security assessments and monitoring.
Encrypt Sensitive Data:
Ensure data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
Use Cloud-Native Security Tools:
Leverage security tools provided by CSPs for enhanced protection.
Recommendations for Cloud Providers to Support Their Customers’ Security Needs
Provide Clear Documentation:
Offer detailed guides on the shared responsibility model.
Offer Robust Security Features and Tools:
Ensure availability of security tools that customers can utilize.
Maintain Transparency:
Share information about security practices and certifications.
Provide Regular Security Updates and Patches:
Keep services secure with timely updates.
Tools and Resources to Aid in Fulfilling Shared Responsibilities
Tools such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), identity management solutions, and encryption services play a vital role in fulfilling shared responsibilities. These tools help in monitoring, managing, and securing cloud resources effectively.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges in Implementing the Shared Responsibility Model
Misunderstanding of Security Responsibilities:
Customers may be unclear about their specific security duties.
Lack of Visibility into Cloud Environments:
Difficulty in monitoring and managing cloud resources effectively.
Complexity of Multi-Cloud Deployments:
Managing security across multiple cloud platforms can be challenging.
Solutions and Best Practices to Overcome These Challenges
Regular Training on Cloud Security Responsibilities:
Educate teams about their roles and the shared responsibility model.
Implementing Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools:
Use CSPM tools to gain better visibility and control over cloud security.
Adopting a Unified Security Approach Across All Cloud Environments:
Standardize security practices across different cloud platforms.
Best Practices for Managing Shared Responsibility:
Implementing consistent security policies and procedures across all cloud services.
Real-World Examples or Case Studies Illustrating Successful Management of Shared Responsibilities
Organizations that have effectively implemented the shared responsibility model often showcase significant improvements in their cloud security posture. For instance, Company XYZ leveraged CSPM tools to monitor their cloud infrastructure, leading to a 40% reduction in security incidents. By clearly defining roles and maintaining open communication channels, they overcame challenges related to multi-cloud security management.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points Discussed About Shared Responsibility in Cloud Computing
In this article, we explored the definition and importance of shared responsibility in cloud computing. We delved into the cloud security responsibility model, defined the roles of cloud providers and customers, discussed cloud computing security roles, best practices for managing shared responsibility, and addressed common challenges faced in implementing this model.
Emphasis on the Importance of Clear Understanding and Collaboration Between Cloud Providers and Customers
Clear delineation and collaboration between cloud providers and customers are vital for effective cloud security. By understanding and adhering to their respective responsibilities, both parties can ensure the protection of data and maintain compliance with relevant regulations.
Encouragement for Readers to Assess and Strengthen Their Own Shared Responsibility Practices
Readers are encouraged to evaluate their current shared responsibility practices and implement the best practices discussed to enhance their cloud security. Assessing and strengthening these practices will position organizations to better mitigate risks and leverage cloud computing’s full potential securely.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, cloud computing can be secure when proper security measures are implemented by both cloud providers and customers. Cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure, but customers must also follow best practices to protect their data and applications. -
What are the top cloud providers?
The leading cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Each offers a range of services and tools to support various cloud computing needs. -
Can small businesses benefit from cloud computing?
Absolutely! Cloud services offer affordable, scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes. Small businesses can leverage cloud computing to access advanced technologies without significant upfront investments in infrastructure.