“`html
Public Cloud: Definition and Examples
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Public cloud provides scalable and cost-effective IT resources over the internet.
- It offers benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and reduced overhead costs.
- Major providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Understanding public cloud architecture is essential for leveraging its capabilities effectively.
- Public cloud use cases span across various industries, enhancing operations and innovation.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Public Cloud Computing?
- Public Cloud Architecture
- Benefits of Public Cloud
- Public Cloud Providers
- Examples of Public Cloud Services
- Public Cloud Use Cases
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
In the digital era, the rise of cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate, innovate, and scale. Understanding the Public cloud definition and examples is crucial for leveraging modern technology solutions. The public cloud enables organizations to access vast computing resources on-demand, reducing costs and fostering innovation.
What is Public Cloud Computing?
Public cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources from third-party providers over the internet. Unlike private cloud or hybrid cloud models, public cloud utilizes a shared infrastructure, allowing multiple customers to access resources simultaneously, a concept known as multi-tenancy. Key characteristics include:
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: Flexible payment based on usage.
- Self-service provisioning: Users can independently manage resources.
- High scalability and elasticity: Resources can scale dynamically to meet demand.
- Shared infrastructure: Resources are shared among multiple customers securely.
According to research, “Public cloud is a type of cloud computing where IT services and infrastructure are provided by third-party vendors over the public internet.”
Public Cloud Architecture
The public cloud architecture comprises several foundational components that work in harmony to deliver scalable and reliable services:
- Virtualization layer: Abstracts physical hardware to create virtual machines.
- Distributed storage systems: Ensure data availability and redundancy.
- Network infrastructure: Facilitates connectivity and data transfer.
- Management and orchestration tools: Automate resource allocation and service deployment.
- Multi-tenant environment: Allows resource sharing among multiple customers securely.
These components work together to provide scalability, resource pooling, and high availability. Concepts like scalability, multi-tenancy, and resource pooling are integral to public cloud architecture. As stated in TechTarget on Public Cloud, “Public cloud architecture typically consists of virtualization layer, distributed storage systems, network infrastructure, management and orchestration tools, and a multi-tenant environment.”
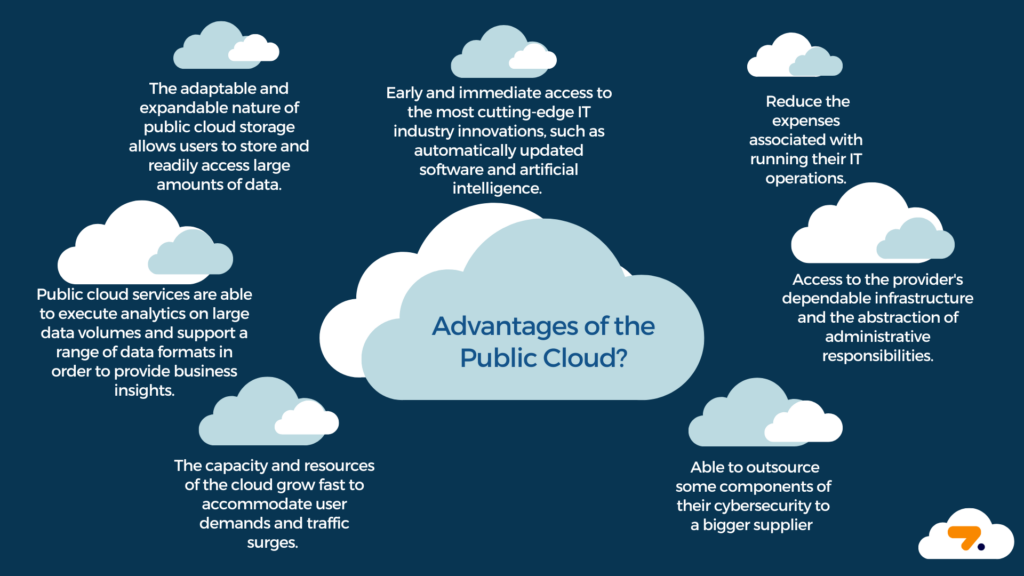
Benefits of Public Cloud
The benefits of public cloud are numerous, offering substantial advantages to businesses of all sizes:
- Cost-effectiveness: Eliminates the need for upfront infrastructure investments. Example: Startups can launch applications without purchasing hardware.
- Scalability and flexibility: Resources can be scaled up or down based on demand. Example: Handling peak traffic during holiday seasons.
- Reliability and uptime: Built-in redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities ensure high availability. Example: Netflix’s use of AWS for reliable content streaming.
- Security measures: Robust security protocols and compliance certifications provided by major providers. Example: Data encryption and access controls.
- Ease of deployment and management: Quick deployment of services without extensive setup. Example: Rapid development and testing environments.
Research findings highlight that “Public cloud offers cost-effectiveness, scalability, reliability, global reach, and access to innovation.” For more details, visit TechTarget on Public Cloud Benefits.
Public Cloud Providers
Major public cloud providers dominate the market, each with unique strengths and market positions:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): The market leader with a comprehensive service portfolio.
- Microsoft Azure: Strong in enterprise solutions and hybrid cloud scenarios.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Renowned for data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
- IBM Cloud: Focuses on enterprise-grade cloud solutions.
- Oracle Cloud: Specializes in database and business applications.
These providers offer varied services, strengths, and target markets, enabling businesses to select solutions that best fit their needs. Additional providers like Alibaba Cloud and Salesforce Cloud also play significant roles in the public cloud ecosystem. As stated in TechTarget on Public Cloud Providers, “The public cloud market is dominated by Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.”
Examples of Public Cloud Services
Major public cloud providers offer a wide range of services to address diverse business needs:
- Compute Services:
- Amazon EC2: Scalable virtual servers.
- Azure Virtual Machines: Windows and Linux VM hosting.
- Google Compute Engine: High-performance virtual machines.
- Storage Solutions:
- Amazon S3: Object storage with high durability.
- Azure Blob Storage: Scalable object storage for unstructured data.
- Google Cloud Storage: Unified object storage.
- Databases:
- Amazon RDS: Managed relational databases.
- Azure SQL Database: Fully managed SQL databases.
- Google Cloud Spanner: Globally distributed relational database.
- Networking Services:
- Amazon VPC: Virtual private cloud for isolated networking.
- Azure Virtual Network: Network isolation and segmentation.
- Google Cloud VPC: Scalable networking solutions.
- Machine Learning and AI Services:
- Amazon SageMaker: Machine learning model development.
- Azure Machine Learning: End-to-end machine learning platform.
- Google AI Platform: Integrated AI tools and services.
These services cater to various business needs, including application development, data management, and advanced analytics. As noted in TechTarget on Public Cloud Services, “Public cloud providers offer a wide range of services including compute, storage, databases, networking, and AI/ML.”
Public Cloud Use Cases
Various industries leverage public cloud use cases to enhance operations and drive innovation:
- Web and Mobile Application Hosting: Deploying scalable applications with global reach. Example: Hosting a mobile app backend on AWS.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Ensuring data protection and quick recovery. Example: Using Azure for automated backups.
- Big Data Analytics: Processing and analyzing large datasets. Example: Utilizing Google BigQuery for data analysis.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Deployments: Managing IoT devices and data streams. Example: Implementing AWS IoT Core for device management.
- Software Development and Testing: Creating environments for development and continuous integration. Example: Using Azure DevOps for automated testing.
Real-world case studies illustrate the effective use of public cloud across various sectors:
- E-commerce: Scaling during peak shopping periods.
- Media Streaming: Handling global content delivery efficiently.
- Finance: Running complex risk analysis models.
- Healthcare: Managing patient data and supporting telemedicine.
- Manufacturing: Implementing IoT and predictive maintenance systems.
As highlighted in research, “Netflix uses AWS to stream content to millions of users worldwide, showcasing the scalability of public cloud solutions.” For more details, visit TechTarget on Public Cloud Use Cases.
Conclusion
In summary, the public cloud definition and examples discussed highlight its pivotal role in modern business operations. Understanding the benefits, architecture, providers, and use cases of public cloud is essential for making informed business decisions. Embracing public cloud solutions can significantly enhance business operations, scalability, and innovation. To get started, consider consulting with cloud experts or initiating a trial with a public cloud provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the public cloud?
The public cloud refers to cloud computing services offered by third-party providers over the public internet, enabling scalable and flexible IT resources. - What are the main benefits of using a public cloud?
The main benefits include cost-effectiveness, scalability, flexibility, reliability, and access to advanced technologies like AI and machine learning. - Who are the leading public cloud providers?
Leading providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
“`