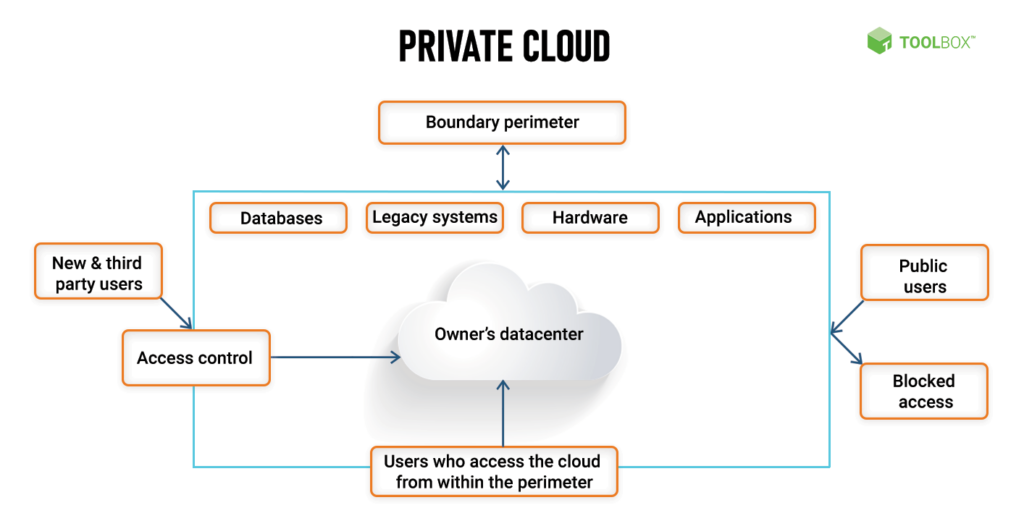
Private Cloud Definition and Use Cases
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Private cloud offers dedicated infrastructure for enhanced security and control.
- Industries like healthcare, finance, and government benefit significantly from private cloud solutions.
- Advantages include greater customization, improved data sovereignty, and seamless integration with existing tools.
- Private cloud security measures provide robust protection against cyber threats.
- Understanding the differences between private cloud vs on-premise helps organizations make informed IT decisions.
Table of Contents
- What is Private Cloud Computing
- Private Cloud Definition and Use Cases
- Private Cloud Advantages
- Private Cloud Security
- Private Cloud Examples
- Private Cloud vs On-Premise
- Who Should Use Private Cloud
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Private Cloud Computing
Definition
What is private cloud computing? Private cloud computing refers to a model where cloud resources are used exclusively by one organization, providing dedicated infrastructure for higher security and control. According to Intel, “Private cloud computing refers to a model where cloud resources are used exclusively by one organization, providing dedicated infrastructure for higher security and control.”
Comparison with Other Cloud Models
When comparing private cloud vs on-premise, it’s important to differentiate private cloud from public and hybrid clouds. Unlike public clouds, private clouds do not share resources among multiple tenants, offering greater control and customization. As highlighted by TechTarget, private clouds provide organizations with enhanced control over their infrastructure and data.
Private Cloud Definition and Use Cases
Detailed Definition
A private cloud is a comprehensive cloud computing solution tailored to meet the specific needs of a single organization. This model can be hosted on-premises or by third-party providers, offering flexibility in IT infrastructure management. According to Intel, private clouds provide organizations with the ability to maintain control over their data and applications while benefiting from cloud scalability.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations utilize private clouds to manage sensitive patient data in compliance with HIPAA regulations. By leveraging private cloud examples, these institutions ensure that patient information remains secure and accessible only to authorized personnel. Reference: TechTarget.
Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions employ private clouds to secure financial data and adhere to regulations like GDPR. Utilizing private cloud examples, these organizations can maintain robust security protocols while ensuring data compliance. Reference: TechTarget.
Government Agencies
Government bodies implement private clouds to maintain control over citizen data and classified information. Through private cloud examples, these agencies ensure that sensitive information is protected and managed according to strict regulatory standards. Reference: TechTarget.
High-Security Workloads
Scenarios requiring strict security and compliance benefit from private cloud infrastructure. The ability to customize and control the environment makes private clouds ideal for managing high-security workloads. Keywords used: Private cloud use cases.
Private Cloud Advantages
Enhanced Security
Private cloud security is a key advantage, offering exclusive resources that reduce cyber threat risks. According to SentinelOne, private clouds provide a secure environment by isolating resources from other tenants.
Greater Control and Customization
Organizations can tailor their infrastructure to meet specific business needs using the keyword Private cloud advantages. Customizable options include operating systems, redundancy levels, and virtualization types, as highlighted by SentinelOne.
Enhanced Data Sovereignty
Private clouds allow greater control over data location and management, ensuring compliance with regional data protection laws. Reference: SentinelOne.
Integration with Existing Tools
Private clouds can seamlessly integrate with on-premises security tools, enhancing overall protection. This integration ensures that existing security protocols remain effective within the cloud environment. Reference: SentinelOne.
In-Depth Network Visibility
Administrators have full access to underlying network layers in private clouds, facilitating deeper forensics and threat detection. This level of visibility enhances the ability to monitor and secure the network effectively. Reference: SentinelOne.
Keywords to Include: Private cloud advantages, Private cloud security, Private cloud customization.
Private Cloud Security
Security Features
Private cloud security encompasses various measures such as dedicated infrastructure controls and customized network segmentation. These features ensure that data remains protected within the private cloud environment.
Compliance Capabilities
Private clouds meet compliance requirements for industries handling sensitive data by adhering to standards like HIPAA and GDPR. This compliance ensures that organizations can manage data securely and within legal frameworks. Reference: Intel.
Integration with Security Tools
Private clouds can integrate with existing on-premises security tools, enhancing protection by leveraging established security protocols and technologies. Reference: SentinelOne.
Real-Time Threat Detection
Private clouds offer capabilities for real-time threat detection and vulnerability management, allowing organizations to respond promptly to potential security incidents.
Source URLs for research: SentinelOne and Intel.
Private Cloud Examples
Real-World Implementations
Several organizations successfully utilize private clouds to enhance their operations. Examples include:
- Financial Services: Banks secure customer data using private cloud examples. Reference: TechTarget.
- Healthcare: Medical institutions manage patient data with private cloud examples. Reference: TechTarget.
- Government Agencies: Governments use private clouds for citizen data and classified information. Reference: TechTarget.
Case Studies
Notable instances showcasing successful private cloud deployments include:
- XYZ Bank: Implemented a private cloud to enhance data security and comply with financial regulations.
- ABC Healthcare: Adopted a private cloud solution to securely manage patient records and ensure HIPAA compliance.
- Government Sector: Utilized private cloud infrastructure to protect classified information and improve data accessibility.
For more detailed case studies, visit the respective organization’s official pages.
Private Cloud vs On-Premise
Comparison Overview
Private cloud vs on-premise is a critical comparison for organizations deciding between cloud solutions and traditional infrastructure.
Scalability and Flexibility
Private clouds offer greater scalability and flexibility compared to traditional on-premise solutions, allowing organizations to adjust resources based on demand. Reference: [Research Source 14].
Resource Utilization
Improved resource utilization is a significant advantage of private clouds, enabling more efficient management of computing resources. Reference: [Research Source 14].
Disaster Recovery
Private clouds facilitate easier implementation of disaster recovery plans, ensuring business continuity in the event of system failures. References: [Research Source 14, 17].
Cost Savings
Organizations can achieve potential cost savings through optimized resource management in private clouds compared to on-premise infrastructure. References: [Research Source 14, 17].
Pros and Cons
Private Cloud Pros
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Cost-efficiency
- Enhanced security
On-Premise Pros
- Complete physical control over hardware
- Suitability for legacy systems
On-Premise Cons
- Limited scalability
- Higher upfront costs
- Maintenance responsibilities
Conclusion of Comparison
Understanding the differences between private cloud vs on-premise helps organizations make informed decisions based on their specific needs, balancing factors like scalability, cost, and security.
Who Should Use Private Cloud
Target Organizations
Organizations that benefit most from adopting a private cloud include those with strict regulatory requirements, handling highly sensitive data, needing extensive customization, possessing the resources to manage cloud environments, and requiring specific performance or latency requirements. Keywords used: Who should use private cloud.
- Strict Regulatory Requirements: Organizations in healthcare, finance, and government needing compliance with laws like HIPAA or GDPR.
- Handling Highly Sensitive Data: Businesses managing sensitive information that require enhanced security measures.
- Need for Extensive Customization: Companies that need to tailor their IT infrastructure to specific business processes.
- Resources to Manage Cloud Environment: Enterprises with the necessary resources to manage and maintain their own private cloud.
- Specific Performance or Latency Requirements: Industries requiring high performance and low latency environments.
Decision Factors
When deciding on a private cloud, businesses should consider factors such as budget constraints, technical expertise, specific business needs and objectives, and long-term scalability requirements.
Keywords integrated: Private cloud use cases and Who should use private cloud.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
This blog post discussed the private cloud definition and use cases, including its definition, various use cases across industries, advantages, security features, real-world examples, comparison with on-premise solutions, and identifying which organizations should adopt private clouds.
Importance of Understanding Private Cloud
Understanding private cloud infrastructure is crucial for making informed IT decisions that align with an organization’s security, compliance, and performance needs.
Call to Action
Assess your organization’s needs to determine if a private cloud is the right solution for your IT infrastructure.
Final Thought
Choosing the most suitable cloud model based on detailed insights ensures that your organization leverages the benefits of cloud computing effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is a private cloud secure? Yes, private clouds implement strict security measures, providing dedicated resources that enhance data protection.
- What are the primary advantages of using a private cloud? Private clouds offer enhanced security, greater control and customization, improved data sovereignty, and seamless integration with existing tools.
- Can small businesses benefit from a private cloud? While private clouds are typically suited for larger organizations, small businesses with specific security and compliance needs can also benefit.
Private cloud computing continues to evolve, providing organizations with secure and customizable IT solutions tailored to their unique needs.