Hybrid Cloud Meaning and Advantages: A Comprehensive Guide for Modern Businesses
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Hybrid cloud computing combines public and private cloud environments to offer flexibility and scalability.
- It optimizes costs by leveraging public cloud resources for non-critical workloads.
- Enhanced security is achieved by keeping sensitive data on private infrastructure while utilizing public cloud services.
- Hybrid cloud solutions improve disaster recovery and business continuity.
- Various industries, including healthcare and finance, benefit significantly from hybrid cloud adoption.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Hybrid Cloud?
- Hybrid Cloud Computing Overview
- Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
- Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud
- Why Companies Use Hybrid Cloud
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Understanding the hybrid cloud meaning and advantages is essential for businesses navigating today’s dynamic IT landscape.
A hybrid cloud integrates both public and private cloud environments, allowing organizations to harness the benefits of both. This combination provides a flexible, scalable IT infrastructure that can adapt to varying business needs.
In today’s IT landscape, hybrid cloud solutions are increasingly vital for modern enterprises. They offer a balance between control and scalability, enabling businesses to optimize their operations effectively. For a comprehensive understanding, refer to this Hybrid cloud computing overview.
Hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds to create a flexible, scalable IT infrastructure. Source
What is Hybrid Cloud?
A hybrid cloud is an IT architecture that integrates on-premises infrastructure or private cloud services with public cloud platforms. NetApp
Organizations utilize both private and public cloud environments to optimize resources, ensuring sensitive data remains secure while leveraging the scalability of public clouds. This approach, often referred to as Hybrid cloud explained, allows businesses to balance control with flexibility.
Consider a hybrid cloud as a combination of personal and public transportation. Just as you might use a personal car for daily commutes and public transit for long-distance travel to maintain flexibility and efficiency, hybrid cloud allows for optimal resource utilization.
- Keeping sensitive data on private infrastructure.
- Utilizing public cloud for scalability and cost-efficiency.
- Ability to move workloads between environments as needed.
Hybrid Cloud Computing Overview
Hybrid cloud computing overview involves the orchestration of workloads across multiple cloud environments, seamlessly integrating public and private clouds to create a unified ecosystem.
The architecture of hybrid cloud environments consists of several structural components, including:
- Private Cloud or On-Premises Infrastructure: Dedicated resources for sensitive data and critical applications.
- Public Cloud Services: Providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer scalable resources for various workloads.
- Network Connectivity: VPNs and direct connections ensure secure and efficient communication between private and public clouds.
- Management and Orchestration Tools: These tools facilitate the seamless management of resources across different environments.
Hybrid cloud integrates public and private clouds to create a unified ecosystem, enabling businesses to leverage the strengths of both environments. Source
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
The Benefits of hybrid cloud are manifold, providing organizations with enhanced flexibility, cost savings, and improved security.
Flexibility and Scalability
Organizations can scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring they efficiently meet workload requirements. TechTarget
Cost Optimization
By leveraging public cloud resources for non-critical workloads, businesses can reduce capital expenditures and optimize operational costs. IBM
Enhanced Security
Sensitive data can remain on private infrastructure, while public cloud security features help protect against threats. TechTarget
Improved Performance
Workloads can be placed in the most suitable environment to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Cloudian
Compliance and Data Sovereignty
Meeting regulatory requirements by keeping certain data on-premises or in specific geographic locations is easier with hybrid cloud solutions. NetRouting
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
Beyond the basic benefits, the Advantages of hybrid cloud provide significant strategic value to organizations.
Improved Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Hybrid cloud enables robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, ensuring that critical data and applications are protected and can be quickly restored in case of an outage. ScienceLogic
Seamless Workload Management
Managing and optimizing workloads across different environments becomes effortless with hybrid cloud solutions, enhancing operational efficiency. Azure
Innovation Acceleration
Access to public cloud services facilitates faster experimentation and development of new applications, driving innovation within the organization. Cloudflare
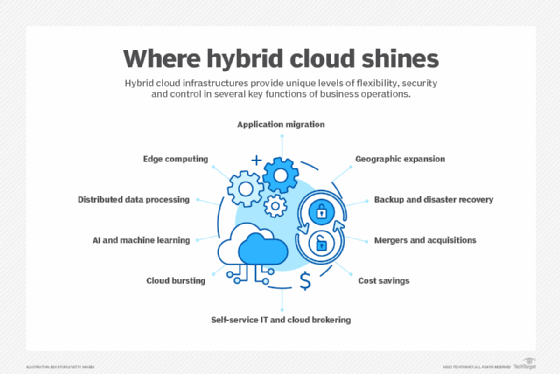
Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
The Hybrid cloud use cases are diverse, covering various applications and industries.
Disaster Recovery and Backup
Utilizing public cloud for off-site data storage and failover ensures that critical systems remain operational during disasters. ScienceLogic
Dev/Test Environments
Leveraging public cloud resources for application development and testing allows for faster iterations and reduced costs. IBM
Big Data Analytics
Processing large datasets using the scalable resources of public clouds enhances data analytics capabilities. Cloudian
Seasonal Demand Management
Handling traffic spikes with cloud bursting capabilities ensures that businesses can maintain performance during peak periods. TechTarget
Industry-Specific Applications
Industries like healthcare, finance, and retail leverage hybrid cloud solutions to meet their unique requirements and regulatory obligations.
Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud
Hybrid cloud vs multi-cloud are often confused, but they serve different purposes in cloud strategies.
Define Both Terms
Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds to provide a unified infrastructure.
Multi-Cloud: Utilizes multiple public cloud providers to distribute workloads and avoid vendor lock-in.
Highlight Key Differences and Similarities
Hybrid cloud focuses on the integration of on-premises and cloud resources, while multi-cloud emphasizes the use of multiple public clouds to distribute workloads. Both strategies aim to optimize resource utilization and enhance flexibility.
For more details, see Cloudian and Azure.
When to Choose Hybrid Cloud Over Multi-Cloud and Vice Versa
Choose hybrid cloud when integration between on-premises and cloud environments is essential for your operations. Opt for multi-cloud to distribute workloads across different public providers, reducing dependency on a single vendor and enhancing resilience.
Consider factors like vendor lock-in, specific service needs, and organizational structure when deciding between hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
Why Companies Use Hybrid Cloud
The adoption of hybrid cloud is driven by various strategic needs, including modernization, cost optimization, and risk mitigation.
Modernization
Transitioning from legacy systems to cloud-native applications enables businesses to leverage modern technologies and improve operational efficiency. IBM
Cost Optimization
Balancing capital and operational expenses through hybrid cloud adoption helps organizations manage costs effectively by utilizing public cloud resources for variable workloads. IBM
Risk Mitigation
Avoiding vendor lock-in and improving system resilience are key benefits of hybrid cloud solutions, reducing the risk of single points of failure. Cloudflare
Compliance
Meeting industry-specific regulatory requirements is simplified with hybrid cloud solutions, allowing organizations to store sensitive data on-premises or in specific geographic locations. NetRouting
Future Trends and Growing Adoption
The trend towards hybrid cloud solutions is on the rise, with businesses increasingly adopting this model to enhance agility and support digital transformation initiatives. Research indicates a continued growth in hybrid cloud adoption, driven by evolving technological needs and business strategies.
Conclusion
Hybrid cloud meaning and advantages encompass a strategic approach to IT infrastructure that balances control, flexibility, and scalability. By integrating public and private cloud environments, businesses can optimize resources, enhance security, and drive innovation.
Organizations should evaluate hybrid cloud solutions to determine how they can meet specific business needs, improve operational efficiency, and support long-term growth objectives.
Call to Action: Explore hybrid cloud solutions today to transform your IT infrastructure and stay competitive in the modern business landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the main differences between hybrid and multi-cloud? Hybrid cloud integrates public and private clouds for a unified infrastructure, while multi-cloud utilizes multiple public cloud providers to distribute workloads and avoid vendor lock-in.
- How does hybrid cloud improve business continuity? By enabling robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, hybrid cloud ensures that critical data and applications remain accessible during outages.
- What industries benefit the most from hybrid cloud? Sectors such as healthcare, finance, and retail significantly benefit from hybrid cloud due to their need for security, compliance, and scalability.
References and Further Reading
- NetApp. “What is Hybrid Cloud?” https://www.netapp.com/hybrid-cloud/what-is-hybrid-cloud/
- IBM. “Hybrid Cloud Architecture.” https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/hybrid-cloud-architecture
- TechTarget. “Hybrid Cloud.” https://www.techtarget.com/searchcloudcomputing/definition/hybrid-cloud
- Cloudian. “What is Hybrid Cloud: Examples, Use Cases, and Challenges.” https://cloudian.com/guides/hybrid-cloud/what-is-hybrid-cloud-examples-use-cases-and-challenges/
- NetRouting. “Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud.” https://netrouting.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-hybrid-cloud/
- ScienceLogic. “Hybrid Cloud Architecture Explained.” https://sciencelogic.com/blog/hybrid-cloud-architecture-explained
- Azure. “What are Private, Public & Hybrid Clouds?” https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/cloud-computing-dictionary/what-are-private-public-hybrid-clouds/
- Cloudflare. “What is Hybrid Cloud?” https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-hybrid-cloud/