Understanding the Differences Between Cloud Models: Public, Private, and Hybrid
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing is essential for modern businesses, offering various deployment models.
- Understanding the differences between cloud models helps organizations choose the right solution.
- Public, private, and hybrid clouds each have unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Choosing the appropriate cloud model depends on factors like security, scalability, and budget.
- A comprehensive cloud model selection guide ensures informed decision-making.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Cloud Computing Models
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Public vs Private vs Hybrid Cloud Differences
- Cloud Deployment Model Comparison
- Cloud Model Selection Guide
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
In today’s digital age, cloud computing plays a pivotal role in enabling businesses to operate efficiently and scale seamlessly. Understanding the differences between cloud models is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage the right cloud infrastructure. This blog post will help you compare cloud computing models, detailing the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Overview of Cloud Computing Models
Definition and Significance of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—such as storage, processing power, and networking—over the internet. This approach offers numerous benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. By utilizing various cloud computing models, organizations can tailor their IT infrastructure to meet specific needs, enhancing operational efficiency.
Introduction to the Three Main Cloud Deployment Models
The primary cloud deployment models are public, private, and hybrid clouds. Each model offers distinct cloud model characteristics that cater to different organizational requirements. This post will delve into each model’s specifics, highlighting their unique features and differences.
Public Cloud
Cloud Model Characteristics
A public cloud refers to cloud services offered by third-party providers over the internet. These services are built on shared resources, enabling multi-tenancy, where multiple organizations use the same infrastructure. Public clouds are renowned for their scalability and pay-as-you-go pricing models, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on demand. According to Google Cloud, public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers, ensuring reliable and scalable services.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Cost-effective, especially for small to medium businesses.
- No upfront infrastructure investments required.
- Rapid scalability to meet changing demands.
Disadvantages:
- Limited control over infrastructure.
- Potential security concerns due to multi-tenancy.
- May not meet strict compliance requirements for certain industries.
Private Cloud
Cloud Model Characteristics
A private cloud is a dedicated cloud environment exclusively for a single organization. This model ensures single-tenancy, providing greater control over infrastructure and security. Private clouds can be either on-premises or hosted by third-party providers, allowing for extensive customization to meet specific organizational needs. As noted by Google Cloud, private clouds offer enhanced control and security, making them suitable for businesses with stringent requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Enhanced security and privacy.
- Ability to meet strict compliance requirements.
- Greater control over performance and resources.
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial costs for infrastructure setup.
- Requires in-house expertise for management.
- Limited scalability compared to public clouds.
Hybrid Cloud
Cloud Model Characteristics
A hybrid cloud combines elements of both public and private cloud environments. This model allows for the integration and seamless sharing of data and applications between the two platforms. Hybrid clouds offer a balance of security, control, and scalability, enabling organizations to optimize their resources effectively. They support workload mobility and optimized resource usage, making them a versatile choice for many businesses, as highlighted by Google Cloud.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Flexibility to choose the optimal environment for each workload.
- Cost optimization by leveraging public cloud for non-sensitive tasks.
- Improved disaster recovery and business continuity.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity in managing multiple environments.
- Potential challenges in data integration and security.
- Requires careful planning and expertise for effective implementation.
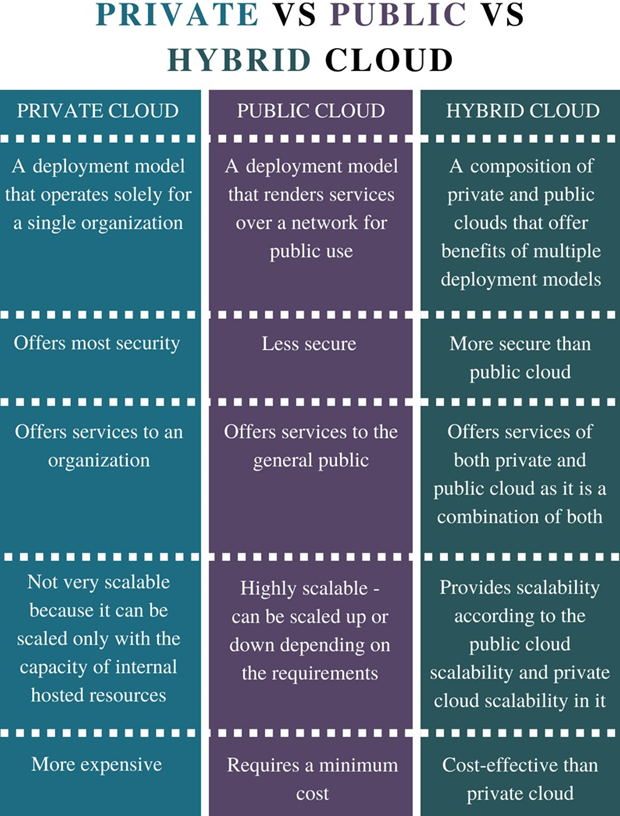
Public vs Private vs Hybrid Cloud Differences
Comparative Analysis
When comparing the three cloud models, several key factors come into play:
- Security: Public clouds offer good security but are shared, private clouds provide the highest control, and hybrid clouds maintain a balanced approach.
- Scalability: Public clouds are highly scalable, private clouds are limited by physical resources, and hybrid clouds offer flexible scaling.
- Cost: Public clouds operate on a pay-as-you-go model with lower upfront costs, private clouds require higher initial investments, and hybrid clouds optimize costs for varied workloads.
- Control: Public clouds offer limited control, private clouds provide full control, and hybrid clouds balance control between environments.
- Compliance: Public clouds may not meet all compliance requirements, private clouds are suitable for strict compliance needs, and hybrid clouds address varied compliance needs.
This comparative analysis helps organizations understand which model aligns best with their security, scalability, and cost requirements. Refer to the comprehensive table below for a side-by-side comparison.
Use Case Scenarios for Each Model
Different organizations benefit from different cloud models based on their unique requirements:
- Public Cloud: Ideal for startups needing cost-effective solutions.
- Private Cloud: Suitable for healthcare organizations requiring strict compliance.
- Hybrid Cloud: Best for enterprises needing both scalability and security.
Cloud Deployment Model Comparison
Detailed Comparison Table
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | Good but shared | Highest control | Balanced |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by physical resources | Flexible scaling |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, lower upfront | Higher initial investment | Optimized for varied workloads |
| Control | Limited | Full control | Balanced |
| Compliance | May not meet all | Suitable for strict | Varied compliance needs |
| Performance | High uptime guarantees | Consistent performance | Optimized performance |
Performance and Reliability
Different cloud models offer varying levels of uptime guarantees and performance metrics such as latency and throughput. Public clouds generally provide high uptime and robust performance due to their extensive infrastructure. Private clouds, while offering consistent performance, may have limitations based on physical resources. Hybrid clouds combine the strengths of both, ensuring reliable and optimized performance across environments.
Cloud Model Selection Guide
Factors to Consider
- Business Requirements: Assess specific needs like data sensitivity and application types.
- Budget: Evaluate total cost of ownership and budget constraints.
- Compliance Needs: Determine regulatory requirements that must be met.
- Scalability Needs: Consider current and future scalability requirements.
- IT Expertise: Assess in-house skills for managing cloud environments.
Decision-Making Framework
- Identify and prioritize business objectives.
- Evaluate workloads and their specific needs.
- Analyze cost implications of each cloud model.
- Assess security and compliance requirements.
- Consider scalability and flexibility needs.
- Review in-house expertise and management capabilities.
- Make an informed decision based on the above factors.
Best Practices
- Conduct thorough planning and assessment.
- Ensure proper security measures are in place.
- Train staff and build necessary expertise.
- Monitor and optimize cloud usage continuously.
Conclusion
The differences between cloud models—public, private, and hybrid—are significant and can greatly impact an organization’s efficiency, security, and cost structure. Choosing the right cloud deployment model based on specific organizational needs is essential for maximizing benefits. Utilize the cloud model selection guide provided to make informed decisions that align with your business objectives. As cloud computing continues to evolve, staying informed about these models will ensure your organization remains competitive and agile.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the main differences between public, private, and hybrid cloud models? Public clouds are shared environments with scalable resources, private clouds offer dedicated infrastructure with enhanced security, and hybrid clouds combine both to balance flexibility and control.
- Which cloud model is best for a startup? A public cloud is typically ideal for startups due to its cost-effectiveness and scalability.
- Can hybrid clouds meet strict compliance requirements? Yes, hybrid clouds can cater to strict compliance needs by utilizing private environments for sensitive data while leveraging public clouds for other tasks.
Call to Action
Ready to optimize your cloud strategy? Assess your current cloud setup and consider the insights provided in this guide. For personalized assistance, schedule a free consultation and take the next step towards a more efficient and secure cloud infrastructure.