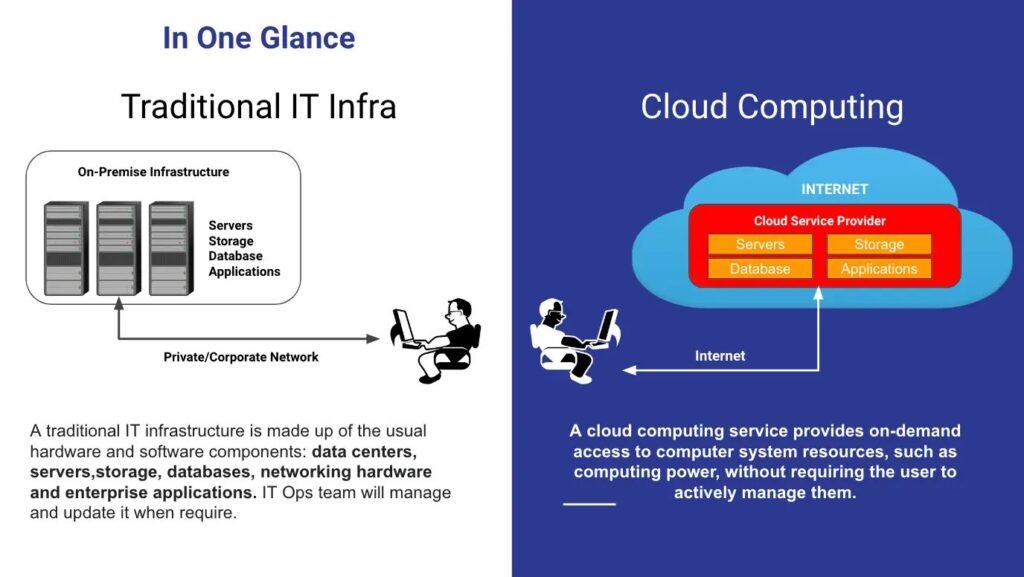
Cloud Computing vs Traditional Computing
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility compared to traditional computing.
- Traditional computing provides more control over infrastructure and data but at higher costs and less flexibility.
- Businesses must evaluate their specific needs, budget, and growth plans when choosing between cloud and traditional computing.
- Hybrid approaches combining both cloud and on-premise solutions can offer the best of both worlds.
- Understanding the differences and implications of each model aids in making informed IT decisions.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Traditional Computing
- Exploring Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing vs On-Premise
- Cloud vs Traditional IT
- Traditional Computing vs Cloud Computing
- Cloud vs Physical Servers
- Cloud vs Legacy Systems
- On-Premise vs Cloud Pros and Cons
- Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, understanding the differences between cloud computing vs traditional computing is crucial for businesses aiming to stay competitive. Choosing between cloud computing vs on-premise solutions can significantly impact a company’s operational efficiency, scalability, and overall IT strategy. With the shift in IT trends leaning towards cloud solutions, this blog will compare and investigate the two models to aid informed decision-making.
Understanding Traditional Computing
Traditional computing, often referred to as on-premise computing, involves the use of physical servers and hardware that are maintained on-site by the organization. This model requires businesses to invest in and manage their own infrastructure, providing them with complete ownership and control over their IT resources.
Key Features:
- Ownership and maintenance of physical hardware by the organization.
- Local installation and operation of software on company-owned machines.
- Data storage on-site with direct control over servers.
- Enhanced control over security and access protocols.
Common Uses and Industries:
- Banking
- Healthcare
- Government sectors
Industries such as banking, healthcare, and government often rely on traditional IT systems due to stringent security and compliance requirements. Common applications include internal databases, legacy systems, and specialized software that require consistent performance and dedicated resources.
Research indicates a longstanding reliance on traditional computing in these sectors, emphasizing the model’s stability and control over data and infrastructure.
Exploring Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics. This model allows businesses to rent access to these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, eliminating the need for owning and maintaining physical infrastructure.
Types of Cloud Services:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Services like virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Platforms that allow developers to build applications without managing underlying infrastructure.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Software applications delivered over the internet, accessible via browsers.
Advantages:
- Flexibility and scalability to adjust resources based on demand.
- Cost-effectiveness with pay-as-you-go models.
- Accessibility from anywhere with internet connectivity.
- Automatic updates and maintenance handled by cloud providers.
Research highlights the growing popularity and benefits of cloud-based solutions in modern businesses, including increased agility and reduced operational costs.
Cloud Computing vs On-Premise
Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud computing allows businesses to scale resources up or down rapidly, adapting to changing demands efficiently. In contrast, on-premise setups require significant planning and investment for expansion.
Cost Implications: The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing contrasts with the substantial initial investments in hardware and infrastructure needed for traditional computing. Over the long term, cloud solutions can offer cost benefits and potential savings.
Implementation Time: Cloud solutions boast faster deployment times compared to the lengthy setup processes required for on-premise systems.
Maintenance and Upgrades: Cloud providers manage maintenance and upgrades, reducing the burden on in-house IT teams, whereas on-premise systems necessitate dedicated personnel for upkeep.
Research Source: Folio3 Blog
Cloud vs Traditional IT
Infrastructure Management: Cloud providers handle most infrastructure management tasks, allowing businesses to focus on core activities. In contrast, traditional IT requires organizations to manage all aspects of their infrastructure.
Security Measures and Compliance Standards: Cloud providers often implement advanced security protocols and compliance standards. Traditional IT offers more direct control over security but demands more in-house expertise to maintain robust security measures.
Maintenance and Update Processes: Cloud systems benefit from automatic updates and maintenance, whereas traditional setups require manual processes for upkeep and upgrades.
Research Source: AWS Whitepapers, TechTarget
Traditional Computing vs Cloud Computing
Performance and Reliability: Traditional computing can offer consistent performance with dedicated resources. Cloud computing, however, provides superior uptime and robust disaster recovery options.
Accessibility and Remote Work Capabilities: Cloud computing excels in supporting remote access and distributed workforces, while traditional computing requires additional setups to enable remote access.
Customization and Control: Traditional computing allows for a higher level of customization and control over systems, whereas cloud computing typically offers more standardized environments.
Research Source: Zenduty Blog, AZ Tech IT Blog
Cloud vs Physical Servers
Hardware Requirements: Cloud computing eliminates the need for extensive physical hardware by providing virtual resources. Traditional computing continues to require ongoing investments in physical servers and equipment.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact: Cloud data centers optimize resource sharing and are more energy-efficient compared to traditional computing, which often has higher energy consumption due to underutilized resources.
Longevity and Lifecycle Management: Virtual resources in the cloud benefit from lifecycle management advantages, whereas on-premise servers experience physical depreciation over time.
Research Source: GlobalDots Blog, BIS Publication
Cloud vs Legacy Systems
Integration Challenges: Integrating legacy systems with cloud solutions can be complex, requiring strategies to overcome compatibility and data transfer issues.
Modernization Benefits: Migrating to the cloud offers opportunities for system modernization and improved operational efficiency.
Case Studies: Organizations that have transitioned from legacy systems to cloud computing often experience enhanced agility, cost savings, and streamlined operations.
Research Source: TutorialsPoint
On-Premise vs Cloud Pros and Cons
Advantages of Traditional Computing:
- Full control over infrastructure and data.
- Potentially lower long-term costs for businesses with stable and predictable workloads.
- No dependence on internet connectivity for accessing systems.
Disadvantages of Traditional Computing:
- High upfront costs for hardware and setup.
- Limited scalability and flexibility.
- Increased responsibility for maintenance and security.
Advantages of Cloud Computing:
- High scalability and flexibility to meet changing business needs.
- Reduced upfront costs with pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Automatic software updates and maintenance handled by providers.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing:
- Dependence on reliable internet connectivity.
- Potential concerns over data security and privacy.
- Less control over infrastructure and underlying hardware.
Considerations for Different Business Sizes and Types: Small businesses may benefit from the cost savings and scalability of cloud computing, while large enterprises might prefer traditional computing for its control and customization. Industry-specific requirements, such as compliance in healthcare, can also influence the choice.
Decision-Making Factors: Key factors include budget, scalability needs, security requirements, and IT expertise. Evaluating these elements helps determine the most suitable computing model for a business’s unique needs.
Research Source: K3 Technologies
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Assessing Business Requirements and Future Growth: Evaluating current and future IT needs involves considering scalability, performance, and budget. Companies should align their computing model with their growth plans and operational demands.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining Cloud and Traditional Computing: A hybrid IT model leverages both cloud and on-premise resources, offering flexibility and the ability to optimize for different workloads. This approach is beneficial in scenarios where certain applications require the control of traditional computing, while others can capitalize on the scalability of the cloud.
Steps to Evaluate and Migrate to the Most Suitable Computing Model:
- Assess current infrastructure and identify needs.
- Select appropriate solutions based on requirements.
- Plan the migration process, ensuring minimal downtime.
- Ensure data integrity and security during the transition.
Research Source: RIGB Blog
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of cloud computing vs traditional computing empowers businesses to make strategic decisions that align with their goals and operational needs. Whether choosing the flexibility of the cloud or the control of traditional systems, it’s essential to assess unique business requirements and consult with IT professionals to determine the best computing model for your organization.
Additional Resources
Further Reading:
Tools and Frameworks:
- Cost calculators
- Migration tools
- Comparison frameworks
Expert Consultations: Consult with IT professionals or cloud service providers for personalized advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is cloud computing secure? Yes, cloud providers implement strict security measures, but users must also follow best practices to ensure data protection.
- What are the top cloud providers? The leading providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Can small businesses benefit from cloud computing? Yes! Cloud services offer affordable, scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes.