“`html
Understanding the Cloud Computing Definition
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing allows businesses and individuals to access computing resources over the internet.
- Understanding the cloud computing definition is crucial in today’s technology-driven world.
- Key terminologies include IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
- Benefits of cloud computing include cost-effectiveness, scalability, and accessibility.
- Common misconceptions about cloud computing can be clarified by understanding the fundamentals.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Cloud Computing Explained Simply
- Key Cloud Computing Terminology
- Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Common Misconceptions
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
Introduction
Understanding the cloud computing definition is essential in today’s technology-driven world.
Many people ask, “How do you define cloud computing?” or “What does cloud computing mean for businesses and individuals?”
Importance of Cloud Computing: Understanding cloud computing is crucial in the current technology landscape.
According to Gartner, cloud computing revenue is expected to grow by 23% in 2023.
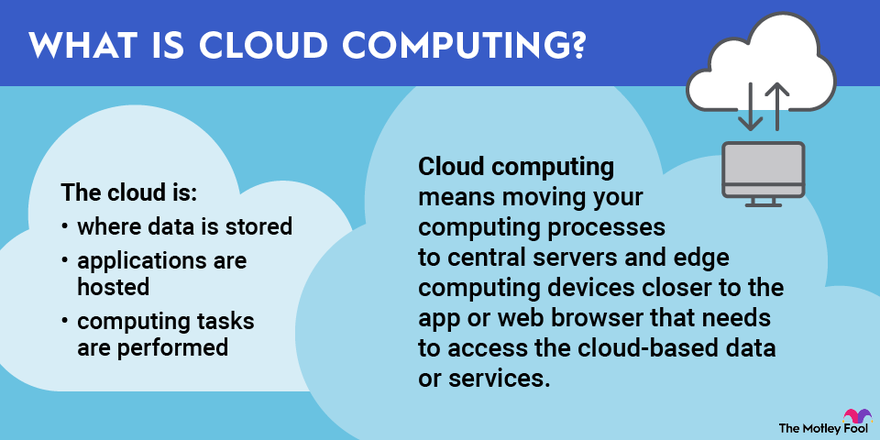
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the Internet (the cloud).
This allows individuals and businesses to define cloud computing, understand its meaning, and explore what cloud computing means in practical terms.
Everyday Terms Explanation: In simpler terms, cloud computing means storing and accessing data and programs over the Internet instead of your computer’s hard drive.
For an authoritative definition, refer to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Cloud Computing Explained Simply
Understanding cloud computing explained simply can help demystify the concept.
Think of cloud computing as a utility service, similar to electricity. Just as you pay for the electricity you use without owning a power plant, cloud computing allows you to use computing resources without owning the infrastructure.
Real-world examples include using Google Photos to store images or subscribing to Microsoft Office 365 for productivity tools.
Accessibility: Cloud computing explanations are straightforward and avoid technical jargon to cater to readers with varying technical backgrounds.
For a simple explanation from a reputable source, visit AWS What is Cloud Computing.
Key Cloud Computing Terminology
Familiarizing yourself with cloud computing terminology is essential for understanding the field.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet.
Example: IaaS provides the foundational infrastructure—servers, storage, and networking resources—that businesses can rent and manage as needed. - PaaS (Platform as a Service): Offers platforms that allow developers to build, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
Example: PaaS offers a framework for developers to create applications efficiently, handling aspects like operating systems and middleware. - SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis.
Example: SaaS includes services like email, customer relationship management (CRM), and collaboration tools that users can access via a web browser. - Public Cloud: Cloud services offered over the public Internet and shared across organizations.
Example: Public clouds are managed by third-party providers and are accessible to multiple tenants. - Private Cloud: Cloud computing resources used exclusively by a single organization.
Example: Private clouds offer enhanced security and control, making them ideal for organizations with strict compliance requirements. - Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private cloud services.
Example: Hybrid clouds allow businesses to leverage the scalability of public clouds while maintaining sensitive data on private infrastructure. - Scalability: The ability to easily increase or decrease IT resources as needed.
Example: Scalability ensures that businesses can adjust their computing resources based on demand without significant delays. - Elasticity: The ability to automatically scale resources up or down based on real-time demand.
Example: Elasticity enables applications to handle varying workloads efficiently, ensuring optimal performance.
For authoritative definitions, refer to Microsoft Azure’s Cloud Glossary.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Exploring the cloud computing definition reveals numerous advantages that contribute to its widespread adoption.
- Cost-effectiveness: Users pay only for the resources they consume.
Example: With cloud computing, businesses can reduce capital expenditures by eliminating the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. - Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Accessibility: Access data and applications from anywhere with an Internet connection.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based backup and recovery solutions protect data.
- Automatic Software Updates: Cloud providers manage software updates and security patches.
Each benefit connects back to the cloud computing definition to reinforce understanding.
Refer to IBM’s Cloud Computing Benefits for more details.
Common Misconceptions
Addressing cloud computing definition and cloud computing explained simply helps dispel common myths.
- Myth 1: “The cloud is not secure.”
Reality: Contrary to this belief, cloud providers often implement more robust security measures than individual businesses can afford.
Research Source: Microsoft on Cloud Security - Myth 2: “Cloud computing is only for large enterprises.”
Reality: Businesses of all sizes, including startups and SMEs, can leverage cloud computing to enhance their operations and reduce costs.
Research Source: AWS Cloud Adoption - Myth 3: “Moving to the cloud is an all-or-nothing decision.”
Reality: Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach, combining cloud and on-premises solutions to meet their specific needs.
Research Source: Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Using the cloud computing definition helps dispel each myth and provides clarity.
Conclusion
In summary, the cloud computing definition, key terminologies, benefits, and clarified misconceptions provide a comprehensive understanding of cloud computing.
Having a clear understanding of cloud computing meaning is vital in the digital age, enabling individuals and businesses to make informed decisions.
We encourage you to delve deeper into cloud computing resources using the provided keywords to expand your knowledge further.
Additional Resources
Credible Links:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Definition of Cloud Computing
- AWS What is Cloud Computing
- Microsoft Azure Cloud Computing Overview
- IBM Cloud Computing Explained
Further Reading:
- “Understanding the Different Types of Cloud Computing Services”
- “A Beginner’s Guide to Cloud Computing Terminology”
- “How Cloud Computing Benefits Small Businesses”
“`