“`html
Cloud Computing Advantages and Disadvantages
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing enables the delivery of computing services over the Internet, fostering innovation and flexibility.
- Scalability and cost savings are primary advantages, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on demand.
- Security, privacy, and dependence on internet connectivity are notable disadvantages that organizations must consider.
- Different service models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS offer varying levels of control and flexibility.
- Evaluating the benefits and risks is crucial for making informed decisions about cloud adoption.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Cloud Computing
- Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Benefits and Risks
- Cloud Service Limitations
- Cloud Computing Challenges
- Evaluating Cloud Computing for Your Business
- Conclusion
- Call to Action
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
Understanding the cloud computing advantages and disadvantages is essential for businesses considering adopting this technology. Evaluating these factors ensures informed decision-making and helps organizations leverage the benefits while mitigating potential risks.
This article delves into the cloud computing advantages and disadvantages, providing a comprehensive overview of the pros and cons of cloud computing to guide your business decisions.
Keywords: Cloud computing advantages and disadvantages, Pros and cons of cloud computing.
Understanding Cloud Computing
At its core, cloud computing is about accessing computing resources via the Internet rather than relying on local servers or personal devices. This paradigm shift allows businesses to utilize IT resources on-demand, providing greater flexibility and efficiency.
There are three primary cloud service models that cater to different business needs:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Offers virtualized computing resources over the Internet. Organizations can rent servers, storage, and networking components, allowing them to scale infrastructure based on demand.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure. This model is ideal for developers focusing on building applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis. Users can access applications like email, CRM, and collaboration tools without installing or maintaining them.
Keywords: Cloud technology advantages, Cloud service limitations.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the standout benefits of cloud computing is its ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. This scalability ensures that businesses can efficiently handle varying workloads without significant upfront investments in hardware.
This flexibility allows organizations to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and business needs, fostering agility and responsiveness.
Cost Savings
Cloud services significantly reduce capital expenditures by eliminating the need for physical hardware and infrastructure. Instead of investing heavily in servers and data centers, businesses can opt for operational expenditures, paying only for the resources they use.
Additionally, the pay-as-you-go pricing model prevalent in cloud services allows for better budget management and cost optimization. Organizations can scale their usage based on actual needs, avoiding overprovisioning and underutilization.
Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud-based solutions enable users to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This level of accessibility breaks down geographical barriers, allowing teams to work seamlessly across different locations.
Enhanced accessibility fosters better collaboration among team members, supports remote work environments, and ensures that critical business operations can continue uninterrupted from any location.
Cloud Technology Advantages
Cloud services often include automatic software updates and maintenance, relieving internal IT teams from routine tasks. This ensures that systems are always up-to-date with the latest features and security patches without manual intervention.
Improved disaster recovery and data backup solutions are integral to cloud offerings. In the event of data loss or system failures, businesses can quickly restore their operations with minimal downtime.
Access to advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is another significant advantage. Cloud platforms provide the computational power and tools necessary to implement these cutting-edge technologies, driving innovation and efficiency.
Cloud Computing Benefits
Cloud computing optimizes resource utilization by efficiently allocating resources based on real-time demand. This ensures that businesses are neither overpaying for unused resources nor under-resourced during peak times.
The agility provided by cloud infrastructure accelerates time-to-market for new products and services. Businesses can deploy solutions faster, respond to market changes promptly, and stay ahead of competitors.
Additionally, scalable cloud solutions enhance a business’s global reach and competitiveness. Organizations can easily expand their operations to new markets without the constraints of physical infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Security and Privacy Concerns
Despite the robust security measures implemented by cloud providers, there are inherent risks related to data breaches and unauthorized access. Sensitive information stored in the cloud can become a target for cyberattacks if not adequately protected.
Ensuring data encryption and compliance with security standards is crucial to safeguard information. Organizations must implement strong security protocols and regularly audit their cloud environments to maintain data integrity and privacy.
Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Cloud services rely heavily on stable and high-speed internet connections. Any disruption in connectivity can severely impact access to critical applications and data, hampering business operations.
Outages or slow internet speeds can lead to decreased productivity and may result in significant operational setbacks, especially for businesses that depend on real-time data access.
Potential Downtime and Reliability Issues
While cloud providers generally offer high availability guarantees, they are not immune to outages. Such downtime can disrupt business operations, leading to potential financial losses and reputational damage.
It’s essential for organizations to have contingency plans in place, such as data backups and disaster recovery strategies, to mitigate the impact of unexpected downtimes.
Cloud Service Limitations
Organizations may face limited control over the underlying infrastructure and services when using cloud providers. This lack of control can hinder customization and optimization tailored to specific business needs.
Vendor lock-in is another significant challenge, where migrating to a different cloud provider can be complex and costly. This dependency can limit an organization’s flexibility and bargaining power.
Compliance issues, especially in regulated industries, arise due to data residency requirements. Ensuring that data is stored and processed in compliance with regional regulations can be challenging when relying on third-party cloud services.
Cloud Computing Challenges
Adopting cloud computing comes with its set of challenges. Integration complexities with existing on-premises systems require significant effort and expertise to ensure seamless operations.
Managing multi-cloud environments adds another layer of complexity, necessitating effective coordination and cost management across different providers to avoid fragmentation and inefficiencies.
Ensuring data sovereignty and compliance with regional regulations is a major challenge, as organizations must navigate varying legal requirements across different jurisdictions.
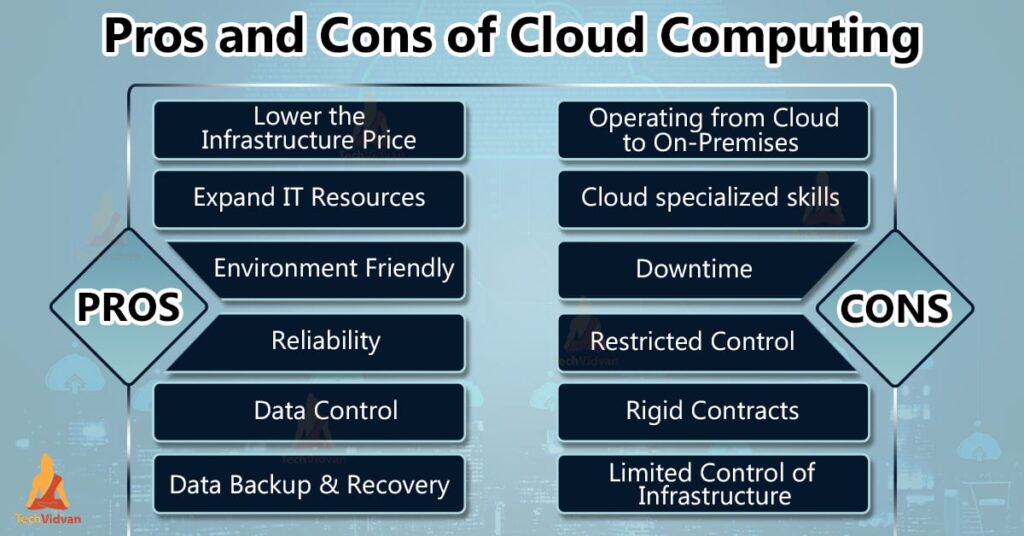
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
To provide a clear overview, here’s a comparative analysis table outlining the main advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Cost efficiency | Security concerns |
| Scalability | Internet dependency |
| Global accessibility | Potential downtime |
| Automatic updates | Limited control |
| Advanced technologies | Compliance challenges |
Keywords: Pros and cons of cloud computing, Cloud computing advantages and disadvantages.
Cloud Computing Benefits and Risks
Delving deeper into the benefits, cloud computing offers improved agility, allowing businesses to respond swiftly to market changes. Access to cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine learning enables organizations to innovate and enhance their services.
Enhanced collaboration is another significant benefit, as cloud platforms facilitate seamless communication and data sharing among team members, regardless of their physical location.
However, these benefits come with associated risks. Data security remains a primary concern, as storing sensitive information in the cloud can make it susceptible to breaches. Vendor dependence is another risk, where reliance on a single cloud provider can limit flexibility and increase vulnerability to service changes.
Compliance issues also pose a challenge, especially for organizations in regulated industries. Ensuring that cloud services meet all necessary legal and regulatory requirements is essential to avoid potential penalties.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement strong security protocols, such as data encryption and regular security audits. Selecting reputable cloud providers with robust security measures is also crucial.
Cloud Service Limitations
Cloud service providers impose certain limitations that organizations must navigate. Restrictions on customization can limit a business’s ability to tailor services to specific needs, potentially hindering operational efficiency.
Data transfer limits are another constraint, where moving large volumes of data to and from the cloud can incur additional costs and impact performance.
Service-level agreements (SLAs) define the expected performance and availability of cloud services. These agreements can significantly impact business operations, as failing to meet SLA terms can lead to penalties or service interruptions.
To overcome these limitations, businesses can negotiate more favorable SLAs or adopt hybrid cloud solutions that combine on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, providing greater flexibility and control.
Cloud Computing Challenges
Adopting cloud computing presents several challenges. One major hurdle is the skill gap in cloud technologies. Organizations often need to invest in training their staff or hiring experts to manage and optimize cloud environments effectively.
Managing cloud costs can also be complex, especially in multi-cloud environments where coordinating expenses across different providers requires meticulous planning and oversight.
Ensuring consistent performance across various cloud platforms while maintaining data sovereignty adds to the complexity. Organizations must navigate regional regulations and ensure that their cloud deployments comply with all relevant laws.
Best practices to address these challenges include investing in comprehensive training programs, implementing robust cost management tools, and adopting governance frameworks that ensure compliance and performance standards are met.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a multitude of benefits but also comes with its share of drawbacks. Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for businesses to leverage the advantages while mitigating the disadvantages effectively.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Cost efficiency | Security concerns |
| Scalability | Internet dependency |
| Global accessibility | Potential downtime |
| Automatic updates | Limited control |
| Advanced technologies | Compliance challenges |
Keywords: Pros and cons of cloud computing, Cloud computing advantages and disadvantages.
Cloud Computing Benefits and Risks
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, including enhanced agility, access to cutting-edge technologies, and improved collaboration. These advantages empower businesses to innovate and operate more efficiently.
However, these benefits are accompanied by risks such as data security concerns, vendor dependence, and potential compliance issues. Data breaches and unauthorized access remain significant threats, necessitating robust security measures.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement strong security protocols, choose reputable cloud providers, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Regular audits and security assessments can further enhance data protection.
Cloud Service Limitations
Cloud service providers impose certain limitations that organizations must navigate. Restrictions on customization can limit a business’s ability to tailor services to specific needs, potentially hindering operational efficiency.
Data transfer limits are another constraint, where moving large volumes of data to and from the cloud can incur additional costs and impact performance.
Service-level agreements (SLAs) define the expected performance and availability of cloud services. These agreements can significantly impact business operations, as failing to meet SLA terms can lead to penalties or service interruptions.
To overcome these limitations, businesses can negotiate more favorable SLAs or adopt hybrid cloud solutions that combine on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, providing greater flexibility and control.
Cloud Computing Challenges
Adopting cloud computing presents several challenges. One major hurdle is the skill gap in cloud technologies. Organizations often need to invest in training their staff or hiring experts to manage and optimize cloud environments effectively.
Managing cloud costs can also be complex, especially in multi-cloud environments where coordinating expenses across different providers requires meticulous planning and oversight.
Ensuring consistent performance across various cloud platforms while maintaining data sovereignty adds to the complexity. Organizations must navigate regional regulations and ensure that their cloud deployments comply with all relevant laws.
Best practices to address these challenges include investing in comprehensive training programs, implementing robust cost management tools, and adopting governance frameworks that ensure compliance and performance standards are met.
Evaluating Cloud Computing for Your Business
When considering cloud adoption, several factors must be evaluated to determine if it’s the right fit for your organization:
- Your organization’s specific needs and goals.
- The sensitivity of your data.
- Compliance requirements in your industry.
- The total cost of ownership compared to on-premises solutions.
- Your team’s readiness for cloud technologies.
To assist in this evaluation, consider the following checklist:
- Assess current infrastructure and identify areas for improvement.
- Determine the types of data to be migrated and their security requirements.
- Review industry-specific compliance standards.
- Calculate potential cost savings and ROI.
- Evaluate the skill level of your IT team and identify training needs.
Keywords: Evaluating cloud computing, Cloud computing advantages and disadvantages.
Incorporate relevant research points such as those from [2] and [3] to support your evaluation criteria.
Conclusion
In summary, cloud computing advantages and disadvantages play a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s IT strategy. The benefits of scalability, cost savings, and accessibility are counterbalanced by challenges related to security, compliance, and dependence on internet connectivity.
Making an informed decision about cloud adoption requires a thorough understanding of these factors and how they align with your business needs. By carefully evaluating the benefits and risks, organizations can harness the power of cloud computing to drive innovation and achieve their goals.
Keywords: Cloud computing advantages and disadvantages, Cloud computing benefits and risks.
References:
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[7],
[8],
[9],
[10]
Call to Action
Before deciding on cloud adoption, assess your organization’s specific needs and objectives. Determine whether the benefits align with your business goals and if your team is prepared to manage cloud environments effectively.
For further exploration of cloud computing, consider consulting with cloud service providers or engaging IT professionals specializing in cloud migrations. These resources can provide personalized guidance and support to ensure a smooth transition to the cloud.
Keywords: Cloud computing challenges, Cloud computing advantages.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, cloud providers implement strict security measures, including data encryption and regular security audits. However, users must also adhere to best practices to ensure data protection.
-
What are the top cloud providers?
The leading cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), each offering a range of services to meet diverse business needs.
-
Can small businesses benefit from cloud computing?
Absolutely! Cloud services offer affordable, scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes, enabling small businesses to access advanced technologies without significant capital investments.
“`