“`html
How Does the Shared Responsibility Model Work?
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Shared Responsibility Model defines the division of security tasks between cloud providers and customers.
- Understanding this model is crucial for maintaining effective cloud security.
- The model varies depending on the cloud service model (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS).
- Both providers and customers have distinct roles to ensure comprehensive security.
- Misunderstanding the model can lead to security vulnerabilities and compliance issues.
Table of Contents
- How Does the Shared Responsibility Model Work?
- What is the Shared Responsibility Model?
- Shared Responsibility Model Breakdown
- Explaining Cloud Security Responsibilities
- Who is Responsible for Cloud Security?
- Shared Security Framework in Cloud Computing
- Benefits of Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model
- Common Misconceptions about the Shared Responsibility Model
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
How does the shared responsibility model work? Understanding the shared responsibility model is essential in cloud computing.
It defines the division of security tasks between cloud service providers and customers, ensuring that both parties play their part in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Grasping this model is crucial for effective cloud security management.
The shared responsibility model is a framework that delineates the security responsibilities of cloud providers and their customers.
What is the Shared Responsibility Model?
The shared responsibility model is a security framework that clearly defines the security tasks allocated to cloud service providers and their customers.
Its primary purpose is to ensure that both parties are aware of their roles in maintaining a secure cloud environment, preventing overlaps and gaps in security measures.
According to recent research, this model guarantees comprehensive security coverage within cloud environments.
Research findings indicate that the model plays a pivotal role in safeguarding cloud infrastructures.
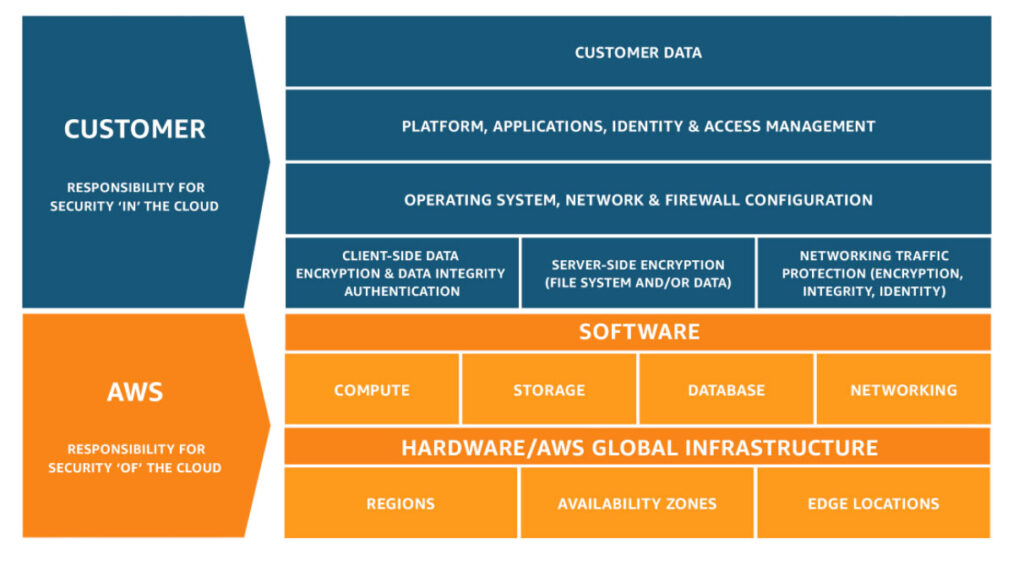
Shared Responsibility Model Breakdown
The shared responsibility model categorizes responsibilities into two main areas:
- Security “of” the Cloud:
- Managed by the Cloud Service Provider (CSP).
- Includes physical security, network infrastructure, hypervisor security, storage, database, networking, and foundational services.
- Security “in” the Cloud:
- Managed by the customer.
- Includes data protection, application security, user access management, and more.
The division of responsibilities varies based on different cloud service models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Different providers implement this division uniquely to cater to their specific service offerings.
Explaining Cloud Security Responsibilities
Cloud Provider Responsibilities
- Physical security of data centers.
- Network infrastructure management.
- Hypervisor security.
- Management of storage, databases, and networking components.
- Maintenance of foundational services.
Each responsibility is backed by robust measures; for instance, data centers are secured with multiple layers of physical defense.
Detailed examples can further elucidate these responsibilities.
Customer Responsibilities
- Data protection and encryption.
- Identity and access management.
- Application security.
- Configuration of networks and firewalls.
- Client-side data encryption.
- Operating system security (in IaaS models).
For example, customers must ensure that their data is encrypted and that access controls are properly configured to prevent unauthorized access.
Specific examples of these tasks highlight the customer’s role in cloud security.
Who is Responsible for Cloud Security?
In the shared responsibility model, cloud providers secure the underlying infrastructure while customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and access controls.
For instance, in the IaaS model:
- Provider: Secures physical hardware and virtualization layers.
- Customer: Secures operating systems, applications, and data.
Similarly, in PaaS and SaaS models, the division of responsibilities shifts, emphasizing a collaborative approach for comprehensive security coverage.
Research emphasizes this collaborative strategy as essential for effective security.
Shared Security Framework in Cloud Computing
The shared security framework supports the shared responsibility model by providing:
- Clear guidelines for security implementations.
- Tools and services for customers to manage their security responsibilities.
- Regular security audits and compliance certifications.
Best practices for implementing this framework include conducting regular security assessments, implementing strong access controls, encrypting sensitive data, and monitoring for security events.
Research highlights the effectiveness of these practices in facilitating robust security management.
Benefits of Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model
- Enhanced Security Posture: Both providers and customers achieve a stronger security stance.
- Clear Accountability: Defined responsibilities reduce the risk of security breaches due to overlooked areas.
- Improved Compliance: Helps in adhering to industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Resources can be allocated more effectively for security measures based on clear responsibilities.
Research findings support each of these benefits, demonstrating that a clear understanding of the shared responsibility model leads to more effective and efficient security management.
Studies show significant improvements in security outcomes when both providers and customers adhere to their defined roles.
Common Misconceptions about the Shared Responsibility Model
Myth 1: The cloud provider handles all security aspects.
Clarification: Customers retain significant responsibilities, especially regarding data protection and access management.
Relying solely on the provider can lead to vulnerabilities in customer-managed areas.
Myth 2: The shared responsibility model is static.
Clarification: Responsibilities can shift based on the specific services used and their implementation.
As cloud services evolve, so do the responsibilities of providers and customers.
Addressing these misconceptions is vital for organizations to implement security measures effectively.
Factual explanations help in dispelling these myths and promoting a clear understanding of the model.
Conclusion
In summary, the shared responsibility model works by clearly defining security tasks between cloud providers and customers.
This delineation ensures that both parties understand their roles in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Clearly defining and adhering to security responsibilities is paramount for achieving a robust cloud security posture.
Embracing this model facilitates comprehensive security coverage and helps organizations effectively manage their cloud resources.
Research findings reinforce the effectiveness of the shared responsibility model in enhancing cloud security.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the primary keyword of the shared responsibility model?
The primary keyword is “How does the shared responsibility model work?” - Who is responsible for cloud security in the shared responsibility model?
Both cloud providers and customers share responsibilities; providers secure the infrastructure, while customers secure their data and applications. - Are there any common misconceptions about the shared responsibility model?
Yes, one common misconception is that cloud providers handle all security aspects, whereas customers have significant responsibilities as well.
“`